A gap decorator allows the annotation of sequences with gap symbols while leaving the underlying sequence unmodified. More...
#include <seqan3/range/decorator/gap_decorator.hpp>
 Inheritance diagram for seqan3::gap_decorator< inner_type >:
Inheritance diagram for seqan3::gap_decorator< inner_type >:Classes | |
| class | gap_decorator_iterator |
| The iterator type over a seqan3::gap_decorator. More... | |
Public Types | |
| using | unaligned_seq_type = inner_type |
| The underlying ungapped range type. | |
Range-associated member types | |
| using | value_type = gapped< value_type_t< inner_type > > |
| The variant type of the alphabet type and gap symbol type (see seqan3::gapped). | |
| using | reference = value_type |
| Use the value type as reference type because the underlying sequence must not be modified. | |
| using | const_reference = reference |
| const_reference type equals reference type equals value type because the underlying sequence must not be modified. | |
| using | size_type = size_type_t< inner_type > |
| The size_type of the underlying sequence. | |
| using | difference_type = difference_type_t< inner_type > |
| The difference type of the underlying sequence. | |
Public Member Functions | |
Constructors, destructor and assignment | |
| constexpr | gap_decorator ()=default |
| Default constructor. Attention: all operations on a solely default constructed decorator, except assigning a new range, are UB. | |
| constexpr | gap_decorator (gap_decorator const &)=default |
| Copy constructor. | |
| constexpr gap_decorator & | operator= (gap_decorator const &)=default |
| Copy construction via assignment. | |
| constexpr | gap_decorator (gap_decorator &&rhs)=default |
| Move constructor. | |
| constexpr gap_decorator & | operator= (gap_decorator &&rhs)=default |
| Move assignment. | |
| ~gap_decorator ()=default | |
| Use default deconstructor. | |
| template<typename other_range_t > | |
| gap_decorator (other_range_t &&range) | |
| Construct with the ungapped range type. | |
| size_type | size () const noexcept |
| Returns the total length of the aligned sequence. More... | |
Iterators | |
| const_iterator | begin () const noexcept |
| Returns an iterator to the first element of the container. More... | |
| const_iterator | cbegin () const noexcept |
| Returns an iterator to the first element of the container. More... | |
| const_iterator | end () const noexcept |
| Returns an iterator pointing behind the last element of the decorator. More... | |
| const_iterator | cend () const noexcept |
| Returns an iterator pointing behind the last element of the decorator. More... | |
Element access | |
| reference | at (size_type const i) |
| Return the i-th element as a reference. More... | |
| const_reference | at (size_type const i) const |
| Return the i-th element as a reference. More... | |
| constexpr reference | operator[] (size_type const i) const noexcept |
| Return the i-th element as a reference. More... | |
Friends | |||||||
Comparison operators | |||||||
Compares two seqan3::gap_decorator 's by underlying sequence and gaps.
ComplexityWorst case: ExceptionsNo-throw guarantee. Does not modify the aligned sequences. | |||||||
| bool | operator== (gap_decorator const &lhs, gap_decorator const &rhs) noexcept | ||||||
Checks whether lhs is equal to rhs. | |||||||
| bool | operator!= (gap_decorator const &lhs, gap_decorator const &rhs) noexcept | ||||||
Checks whether lhs is not equal to rhs. | |||||||
| bool | operator< (gap_decorator const &lhs, gap_decorator const &rhs) noexcept | ||||||
Checks whether lhs is less than rhs. | |||||||
| bool | operator<= (gap_decorator const &lhs, gap_decorator const &rhs) noexcept | ||||||
Checks whether lhs is less than or equal to rhs. | |||||||
| bool | operator> (gap_decorator const &lhs, gap_decorator const &rhs) noexcept | ||||||
Checks whether lhs is greater than rhs. | |||||||
| bool | operator>= (gap_decorator const &lhs, gap_decorator const &rhs) noexcept | ||||||
Checks whether lhs is greater than or equal to rhs. | |||||||
Related Functions | |
(Note that these are not member functions.) | |
Requirements for seqan3::aligned_sequence | |
You can expect these functions on all types that model seqan3::aligned_sequence. | |
| std::ranges::iterator_t< aligned_seq_t > | insert_gap (aligned_seq_t &aligned_seq, typename aligned_seq_t::const_iterator pos_it) |
| Insert a seqan3::gap into an aligned sequence. More... | |
| std::ranges::iterator_t< aligned_seq_t > | insert_gap (aligned_seq_t &aligned_seq, typename aligned_seq_t::const_iterator pos_it, typename aligned_seq_t::size_type size) |
| Insert multiple seqan3::gap into an aligned sequence. More... | |
| std::ranges::iterator_t< aligned_seq_t > | erase_gap (aligned_seq_t &aligned_seq, typename aligned_seq_t::const_iterator pos_it) |
| Erase a seqan3::gap from an aligned sequence. More... | |
| std::ranges::iterator_t< aligned_seq_t > | erase_gap (aligned_seq_t &aligned_seq, typename aligned_seq_t::const_iterator first, typename aligned_seq_t::const_iterator last) |
| Erase multiple seqan3::gap from an aligned sequence. More... | |
| void | assign_unaligned (aligned_seq_t &aligned_seq, unaligned_sequence_type &&unaligned_seq) |
| Assign an ungapped sequence to a gapped sequence. More... | |
Aligned sequence modifications | |
| iterator | insert_gap (const_iterator const it, size_type const count=1) |
| Insert a gap of length count at the aligned sequence iterator position. More... | |
| iterator | erase_gap (const_iterator const it) |
| Erase one gap symbol at the indicated iterator postion. More... | |
| iterator | erase_gap (const_iterator const first, const_iterator const last) |
| Erase gap symbols at the iterator postions [first, last[. More... | |
| template<typename unaligned_seq_t > | |
| void | assign_unaligned (gap_decorator &dec, unaligned_seq_t &&unaligned) |
| Assigns a new sequence of type seqan3::gap_decorator::unaligned_seq_type to the decorator. More... | |
A gap decorator allows the annotation of sequences with gap symbols while leaving the underlying sequence unmodified.
| inner_type | The type of range that will be decorated with gaps; must model std::ranges::random_access_range and std::ranges::sized_range. |
This class may be used whenever you want to store or compute an alignment. The underlying (ungapped) sequence remains unmodified, and is augmented with gap information. The seqan3::gap_decorator behaves just like a vector over a gapped alphabet when iterating over it, inserting/erasing gaps or accessing a position. The only difference lies in the performance and size overhead (see below).
n The length of the underlying sequence. k The number of contiguous gaps (not gap symbols). l The total number of gap symbols.
| access next | random access | gap insert/erase at end | gap insert/erase random | size overhead | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| decorator | 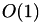 | 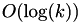 | 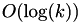 | 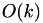 | 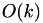 |
| vector | 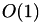 | 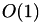 | 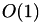 | 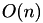 | 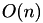 |
The size overhead refers to the space that is needed when using each of the data structures in addition to an already existing ungapped sequence.
This decorator stores a std::set over tuples of (pos, cumulative_size) where every entry represents one contiguous stretch of gaps. pos is the (virtual) insert position in the underlying range and cumulative_size is the length of that contiguous stretch of gaps plus the length of all preceding elements. Resolving random access requires logarithmic access into the set and inserting or removing a gap symbol additionally entails updating all subsequent elements in the set to preserve correct cumulative sizes.
|
inline |
Return the i-th element as a reference.
| i | The element to retrieve. |
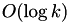 where
where 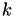 is the number of gaps.
is the number of gaps.
Throws std::out_of_range exception if i is out of range.
|
inline |
Return the i-th element as a reference.
| i | The element to retrieve. |
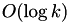 where
where 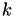 is the number of gaps.
is the number of gaps.
Throws std::out_of_range exception if i is out of range.
|
inlinenoexcept |
Returns an iterator to the first element of the container.
If the container is empty, the returned iterator will be equal to end().
Constant.
No-throw guarantee.
|
inlinenoexcept |
Returns an iterator to the first element of the container.
If the container is empty, the returned iterator will be equal to end().
Constant.
No-throw guarantee.
|
inlinenoexcept |
Returns an iterator pointing behind the last element of the decorator.
Constant.
No-throw guarantee.
|
inlinenoexcept |
Returns an iterator pointing behind the last element of the decorator.
Constant.
No-throw guarantee.
|
inline |
Erase gap symbols at the iterator postions [first, last[.
| [in] | first | The iterator pointing to the position where to start inserting gaps. |
| [in] | last | The iterator pointing to the position where to stop erasing gaps. |
| seqan3::gap_erase_failure | if [first, last[ does not correspond to a consecutive range of seqan3::gap 's. |
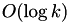
|
inline |
Erase one gap symbol at the indicated iterator postion.
| it | Iterator indicating the gap to be erased. |
| seqan3::gap_erase_failure | if character is no seqan3::gap. |
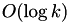
|
inline |
Insert a gap of length count at the aligned sequence iterator position.
| it | Iterator indicating the gap start position in the aligned sequence. |
| count | Number of gap symbols to be inserted. |
Average and worst case (insertion before last gap): 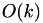 , Best case (back insertion):
, Best case (back insertion): 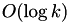 .
.
|
inlineconstexprnoexcept |
Return the i-th element as a reference.
| i | The element to retrieve. |
This function delegates to an iterator seqan3::gap_decorator.
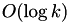 where
where 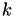 is the number of gaps.
is the number of gaps.
|
inlinenoexcept |
Returns the total length of the aligned sequence.
Constant.
No-throw guarantee.
|
related |
Assign an ungapped sequence to a gapped sequence.
| aligned_seq_t | Type of the container to reassign; must model seqan3::aligned_sequence. |
| unaligned_seq_t | Type of the container to assign from; must correspond to the aligned type without gap information (see details.) |
| [in,out] | aligned_seq | The gapped sequence container to assign to. |
| [in,out] | unaligned_seq | The unaligned sequence container to assign from. |
An aligned sequence has to be assignable from its unaligned counter part. For example a std::vector<seqan3::gapped<seqan3::dna4>> as well as a seqan3::gap_decorator<std::vector<seqan3::dna4>> can be assigned from s std::vector<seqan3::dna4> via seqan3::assign_unaligned.
|
friend |
Assigns a new sequence of type seqan3::gap_decorator::unaligned_seq_type to the decorator.
| [in,out] | dec | The decorator to modify. |
| [in] | unaligned | The unaligned sequence to assign. |
|
related |
Erase multiple seqan3::gap from an aligned sequence.
| aligned_seq_t | Type of the range to modify; must model seqan3::aligned_sequence. |
| [in,out] | aligned_seq | The aligned sequence to modify. |
| [in] | first | The iterator pointing to the position where to start erasing gaps. |
| [in] | last | The iterator pointing to the position where to stop erasing gaps. |
last refers to the last element, the std::ranges::end() iterator is returned.| seqan3::gap_erase_failure | if one of the characters in [first, last) no seqan3::gap. |
|
related |
Erase a seqan3::gap from an aligned sequence.
| aligned_seq_t | Type of the range to modify; must model seqan3::aligned_sequence. |
| [in,out] | aligned_seq | The aligned sequence to modify. |
| [in] | pos_it | The iterator pointing to the position where to erase a gap. |
pos_it refers to the last element, the std::ranges::end() iterator is returned.| seqan3::gap_erase_failure | if there is no seqan3::gap at pos_it. |
|
related |
Insert a seqan3::gap into an aligned sequence.
| aligned_seq_t | Type of the range to modify; must model seqan3::aligned_sequence. |
| [in,out] | aligned_seq | The aligned sequence to modify. |
| [in] | pos_it | The iterator pointing to the position where to insert a gap. |
|
related |
Insert multiple seqan3::gap into an aligned sequence.
| aligned_seq_t | Type of the range to modify; must model seqan3::aligned_sequence. |
| [in,out] | aligned_seq | The aligned sequence to modify. |
| [in] | pos_it | The iterator pointing to the position where to insert a gaps. |
| [in] | size | The number of gap symbols to insert (will result in a gap of length size). |
pos_it if size == 0.