Class Specialization
Automaton
An Automaton has directed edges, labeled with input symbols, and a distinct start state, called root. The
input symbols require the use of a third parameter: The alphabet of the input symbols.
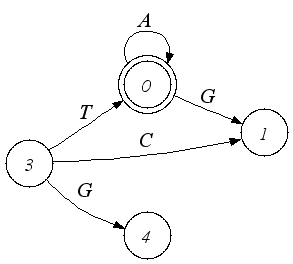 |
| An automaton, where |
 |  | ||||||
Automaton | |||||||
 |  | ||||||
Include Headers
seqan/graph_types.h
Parameters
The alphabet type that is used for the transition labels. Metafunctions: Alphabet Default: Remarks: Use Alphabet to get the type of the labels in an automaton. | |
The cargo type that can be attached to the edges. Metafunctions: Cargo Default: Remarks: Use Cargo to get the cargo type of an undirected graph. | |
The specializing type for the graph. Metafunctions: Spec Remarks: Use WithoutEdgeId here to omit edge ids.
Note: If edges do not store ids external property maps do not work. |
Specialization of
Specializations
| A special automaton that stores words instead of single characters along its edges. |
Metafunctions
| Access to the Alphabet type. (Graph) | |
| Type of additional data stored in an object. (Graph) | |
| Type of an object that represents an edge descriptor. (Graph) | |
| Type of an object that represents an Id Manager. (Graph) | |
| Edge type of a graph object. (Graph) | |
| Type of the object a given object depends on. (Graph) | |
| Type of iterator objects that are used to traverse the container. (Graph) | |
| The spec of a class. (Graph) | |
| Type of an object that represents a vertex descriptor. (Graph) |
Functions
| Adds a new edge to the graph, either with or without cargo. (Graph) | |
| Shortcut to add multiple edges at once. Creates vertices implicitly. (Graph) | |
| Adds a new vertex to the graph. (Graph) | |
| Initializes a vertex map with values of an array. (Graph) | |
| Assigns a new root vertex to the graph. | |
| Initializes a vertex map with values of an array. (Graph) | |
| Test whether an automaton can parse a string completely. | |
| Resets an object. (Graph) | |
| Removes all edges in a graph. (Graph) | |
| Removes all vertices in a graph. (Graph) | |
| Create an interval tree. (Graph) | |
| Creates the root in a tree or an automaton. | |
| Number of incident edges for a given vertex. (Graph) | |
| Test a container for being empty. (Graph) | |
| Finds an edge. (Graph) | |
| Returns an adjacency matrix representation of the graph. (Graph) | |
| Get method for the root of a tree or an automaton. | |
| Gets the successor for a given vertex and an edge label. For an automaton a single character is required whereas for a word graph getSuccessor takes a string. | |
| Number of incoming edges for a given vertex. (Graph) | |
| Tests whether a given vertex is the root or not. | |
| Number of edges in a graph. (Graph) | |
| Number of vertices in a graph. (Graph) | |
| Number of outgoing edges for a given vertex. (Graph) | |
| Parses a string one character at a time and moves accordingly in the automaton. | |
| Removes an edge from the graph. For automatons a label is required. (Graph) | |
| Removes the incoming edges of a given vertex. (Graph) | |
| Removes the outgoing edges of a given vertex. (Graph) | |
| Removes a vertex. (Graph) | |
| Initializes an edge map (Graph) | |
| Initializes a vertex map. (Graph) | |
| Gets a reference to the root of the tree. | |
| Returns the source vertex of an edge. (Graph) | |
| Returns the target vertex of an edge. (Graph) | |
| Transposes a graph, either in-place or from source to dest. (Graph) | |
| Saves records to a file. (Graph) |
Example Programs
Bellman-Ford Algorithm, Longest Increasing Subsequence, Topological Sort, Breadth-First Search, Strongly Connected Components, Transitive Closure, HMM Silent States, Kruskals Algorithm, Heaviest Increasing Subsequence, Floyd-Warshall Algorithm, Maximum Flow, Shortest Path in DAGs, HMM, Prims Algorithm, All Pairs Shortest Path, Depth-First Search, Dijkstras Algorithm, Longest Common Subsequence
SeqAn - Sequence Analysis Library - www.seqan.de